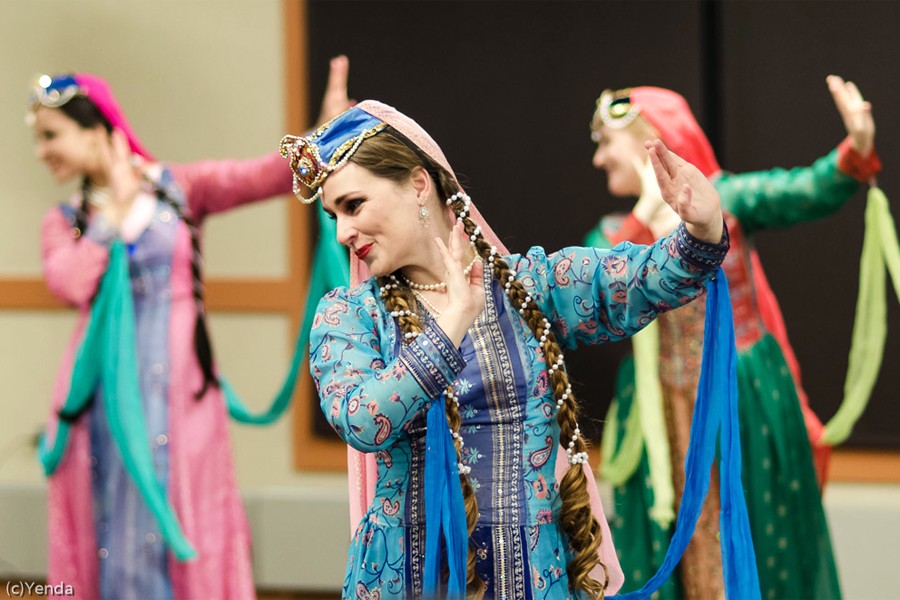
Iran, also called Persia, is a country with multi millennium civilization and diverse ethnics. The culture of Iran is one of the oldest in the world. Owing to its dominant geo-political position and culture in the world, Iran has directly influenced cultures and peoples as far away as Italy, Macedonia, and Greece to the West, Russia to the North, the Arabian Peninsula to the South, and South and East Asia to the East. Thus an eclectic cultural elasticity has been said to be one of the key defining characteristics of the Persian spirit and a clue to its historical longevity. Furthermore, Iran’s culture has manifested itself in several facets throughout the history of Iran as well as the Caucasus, Central Asia, Anatolia, and Mesopotamia.
The article uses the words Persian and Iranian interchangeably, sometimes referring to the language and its speakers, and other times referring to the name of pre-20th century Iran, a nomenclature which survives from western explorers and orientalists. They are not the same and the cultures of the peoples of Greater Persia are the focus of this article.
Art
Iran has one of the richest art heritages in world history and encompasses many disciplines including architecture, painting, weaving, pottery, calligraphy, metalworking and stone-masonry. There is also a very vibrant Iranian modern and contemporary art scene.
Iranian art has gone through numerous phases. The unique aesthetics of Iran is evident from the Achaemenid reliefs in Persepolis to the mosaic paintings of Bishapur. The Islamic era brought drastic changes to the styles and practice of the arts, each dynasty with its own particular foci. The Qajarid era was the last stage of classical Persian art, before modernism was imported and suffused into elements of traditionalist schools of aesthetics.
Language and literature
Several languages are spoken in different regions of Iran. The predominant language and national language is Persian, which is spoken across the country. Azerbaijani is spoken primarily and widely in the northwest, Kurdish primarily in the west as well as Luri, Mazandarani and Gilaki at the Caspian Sea coastal regions, Arabic primarily in the Persian Gulf coastal regions, Balochi primarily in the desolate and remote far southeast, and Turkmen primarily in northern border regions. Smaller languages spread in other regions notably include Talysh, Georgian, Armenian, Assyrian, and Circassian, amongst others.
Persian literature inspired Goethe, Ralph Waldo Emerson, and many others, and it has been often dubbed as a most worthy language to serve as a conduit for poetry. Dialects of Persian are sporadically spoken throughout the region from China to Syria to Russia, though mainly in the Iranian Plateau.
Contemporary Iranian literature is influenced by classical Persian poetry, but also reflects the particularities of modern-day Iran, through writers such as Houshang Moradi-Kermani, the most translated modern Iranian author, and poet Ahmad Shamlou.
Religion
Zoroastrianism was the national faith of Iran for more than a millennium before the Arab conquest. It has had an immense influence on Iranian philosophy, culture and art after the people of Iran converted to Islam.[3]
Today of the 98% of Muslims living in Iran, around 89% are Shi’a and only around 9% are Sunni.This is quite the opposite trend of the percentage distribution of Shi’a to Sunni Islam followers in the rest of the Muslim population from state to state (primarily in the Middle East) and throughout the rest of the world.
Followers of the Christian faith comprise around 250,000 Armenians, around 32,000 Assyrians, and a small number of Roman Catholic, Anglican, and Protestant Iranians that have been converted by missionaries in earlier centuries. Thus, Christians that live in Iran are primarily descendants of indigenous Christians that were converted during the 19th and 20th centuries. Judaism is an officially recognized faith in Iran, and in spite of the hostilities between Iran and Israel over the Palestinian issue, the millennia old Jewish community in Iran enjoys the right to practice their religion freely as well as a dedicated seat in parliament to a representative member of their faith. In addition to Christianity and Judaism, Zoroastrianism is another officially recognized religion in Iran, although followers of this faith do not hold a large population in Iran. In addition, although there have been isolated incidences of prejudice against Zoroastrians, most followers of this faith have not been persecuted for being followers of this faith.
Holidays
The Persian year begins in the vernal equinox: if the astronomical vernal equinox comes before noon, then the present day is the first day of the Persian year. If the equinox falls after noon, then the next day is the official first day of the Persian year. The Persian Calendar, which is the official calendar of Iran, is a solar calendar with a starting point that is the same as the Islamic calendar. According to the Iran Labor Code, Friday is the weekly day of rest. Government official working hours are from Saturday to Wednesday (from 8 am to 4 pm).
Although the date of certain holidays in Iran are not exact (due to the calendar system they use, most of these holidays are around the same time), some of the major public holidays in Iran include Oil Nationalization Day (20 March), Nowrooz—which is the Iranian equivalent of New Years (20 March), the Prophet’s Birthday and Imam Sadeq (4 June), and the Death of Imam Khomeini (5 June). Additional holidays include The Anniversary of the Uprising Against the Shah (30 January), Ashoura (11 February), Victory of the 1979 Islamic Revolution (2 April), Sizdah-Bedar—Public Outing Day to end Nowrooz (1 April), and Islamic Republic Day (20 January).
Wedding ceremonies
There are two stages in a typical wedding ritual in Iran. Usually both phases take place in one day. The first stage is known as “Aghd”, which is basically the legal component of marriage in Iran. In this process, the Bride and Groom as well as their respective guardians sign a marriage contract. This phase usually takes place in the bride’s home. After this legal process is over, the second phase, “Jashn-e Aroosi” takes place. In this step, which is basically the wedding reception, where actual feasts and celebrations are held, typically lasts from about 3–7 days. The ceremony takes place in a decorated room with flowers and a beautifully decorated spread on the floor. This spread is typically passed down from mother to daughter and is composed of very nice fabric such as “Termeh” (cashmere), “Atlas” (gold embroidered satin), or “Abrisham” (silk).
Items are placed on this spread: a Mirror (of fate), two Candelabras (representing the bride and groom and their bright future), a tray of seven multi-colored herbs and spices (including poppy seeds, wild rice, angelica, salt, nigella seeds, black tea, and frankincense). These herbs and spices play specific roles ranging from breaking spells and witchcraft, to blinding the evil eye, to burning evil spirits. In addition to these herbs/spices, a special baked and decorated flatbread, a basket of decorated eggs, decorated almonds, walnuts and hazelnuts (in their shell to represent fertility), a basket of pomegranates/apples (for a joyous future as these fruits are considered divine), a cup of rose water (from special Persian roses)—which helps perfume the air, a bowl made out of sugar (apparently to sweeten life for the newlywed couple), and a brazier holding burning coals and sprinkled with wild rue (as a way to keep the evil eye away and to purify the wedding ritual) are placed on the spread as well. Finally, there are additional items that must be placed on the spread, including a bowl of gold coins (to represent wealth and prosperity), a scarf/shawl made of silk/fine fabric (to be held over the bride and groom’s head at certain points in the ceremony), two sugar cones—which are ground above the bride and groom’s head, thus symbolizing sweetness/happiness, a cup of honey (to sweeten life), a needle and seven strands of colored thread (the shawl that is held above the bride and groom’s head is sewn together with the string throughout the ceremony), and a copy of the couple’s Holy Book (other religions require different texts); but all of these books symbolize God’s blessing for the couple. An early age in marriage—especially for brides—is a long documented feature of marriage in Iran. While the people of Iran have been trying to legally change this practice by implementing a higher minimum in marriage, there have been countless blocks to such an attempt. Although the average age of women being married has increased by about five years in the past couple decades, young girls being married is still common feature of marriage in Iran—even though there is an article in the Iranian Civil Code that forbid the marriage of women younger than 15 years of age and males younger than 18 years of age.
Persian rugs
Iranians were some of the first people in history to weave carpets. First deriving from the notion of basic need, the Persian rug started out as a simple/pure weave of fabric that helped nomadic people living in ancient Iran stay warm from the cold, damp ground. As time progressed, the complexity and beauty of rugs increased to a point where rugs are now bought as decorative pieces. Because of the long history of fine silk and wool rug weaving in Iran, Persian rugs are world-renowned as some of the most beautiful, intricately designed rugs available. Around various places in Iran, rugs seem to be some of the most prized possessions of the local people. Iran currently produces more rugs and carpets than all other countries in the world put together.
We, at Iran Traditional Hotels, are more than happy to give you more information and help you arrange your visit from Iran.
To organize your tailored-made trip to Iran, please click here.